 |
Monitoring registry changes is
sometimes necessary to detect intruders or if an Unknown
process / application is resetting a registry value every time (say,
the Internet Explorer Favorites Shell folder location is changed on
every startup). You can set a registry audit policy for a specific
registry key in order to track down information about the registry
change event. Phase I:
Enable Audit Policy
-
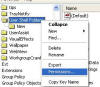
Click Start, Run and type
Secpol.msc (or via
GPEDIT.MSC)
-
In the left pane, under Local
Policies, click Audit Policy
-
In the right pane,
double-click Audit Object Access
-
Select the Success and Failure
boxes
Phase II: Setting the Audit for
registry key(s)
-
Click Start, Run and type
Regedit and navigate to the
key you want to audit
-
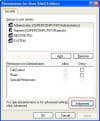
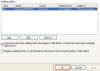
On the Edit menu, click
Permission, click Advanced.
-
On the Auditing tab, click
Add.
-
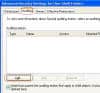
Type your username there and
add it to the audit list
-
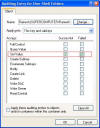
In the Auditing Entry For Name
dialog, in the Access list, select both the Successful and
Failed check boxes next to the activities for which you want to
audit successful and failed attempts.
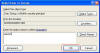
(Example: If you want to
track the write events for a registry value, enable the SetValue
activity from the list )
Now that you've set an audit
successfully. Work normally in the system as usual. If the behavior
is see (say for example, the Favorites location value is overwritten
by a software ), it's time to inspect the Event Log (Security log
which contains the Security audit information). Proceed to Phase
III
Phase III: Inspect the Event Logs for any information on the
changed keys/values:
-
Click Start, Run and type
Eventvwr.msc
-
In Event Viewer's left pane,
click Security.
-
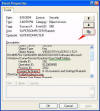
In the right-pane,
double-click the appropriate entry to see more details. You can
spot the entry by matching the time / date and the Image File
Name seen in the log.
-
In the Security log, the
Image File Name reveals the
name of the program which had tried to change (or changed) the
registry key/value silently
|